
Vista and Windows 7 Basics
Windows 95 was an exciting evolution for operating systems in a large part because of its exciting new Graphical User Interface (GUI) environment called the desktop. Each subsequent operating system released by Microsoft has improved upon the desktop by either adding more features or by improving features that already existed. Vista's Desktop is no exception and has been improved by adding new visual features and improved functionality with Windows Aero, a Sidebar with gadgets feature, an improved Control Panel, an Instant Search feature, along with a reconfigured Taskbar and Start menu.
The new visual aspects of Windows Aero such as Windows Glass transparency, increased visual controls, and more visual previews is infused in every aspect and feature of Vista's desktop and remains a staple in Windows 7. These aspects can be personalized by reconfiguring the desktop to fit a user's needs.
- Windows Aero
Windows Aero, Vista's graphical user interface, includes a new transparency effect called Aero Glass. All of the graphics of the desktop and the features windows have sharper and clearer graphics than any previous versions of Windows operating systems. There are also more graphics in every aspect of the desktop such as visual thumbnails that provide a preview of the application for a taskbar button when the mouse pointer is over it, improved Details and Preview Panes in Explorer to see what is in files, a new feature called Flip which shows a view of every available window, and the Flip 3D feature which shows a rotating 3D view of every available window.
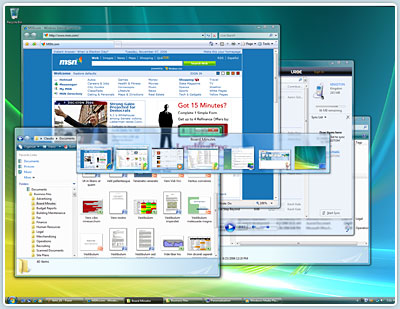
Windows Vista Flip
Windows Vista Taskbar Thumbnails
- Windows Vista Sidebar
Vista's Sidebar is a way to access information quickly on the desktop by using customizable programs called gadgets. Default gadgets included with Vista inclulde the weather, a clock, a calendar, a slide show of pictures, a CPU meter, contacts, picture puzzles, notes, a currency converter, news headlines, and a stock monitor. Other gadgets can be found and downloaded from a variety of sites, or gadgets can be created by creating and packaging an .html and .xml file. More specific information on developing gadgets can be found at the Microsoft Developer Network web site.
In order to open the Sidebar click on Start-->All Programs-->Accessories-->Windows Sidebar or enter "sidebar" into the Instant Search box. Sidebar can be kept on top of or beneath all windows by clicking Start-->Control Panel-->Appearance and Personalization-->Windows Sidebar Properties, and selecting the Sidebar is always on top of other windows check box.
Individual gadgets can always be on top from the Windows Sidebar Properties window by right clicking a gadget and selecting Always on Top. Gadgets can also be placed on the desktop instead of in the Sidebar by right clicking the gadget, selecting Detach from Sidebar, and dragging the gadget to the desktop.
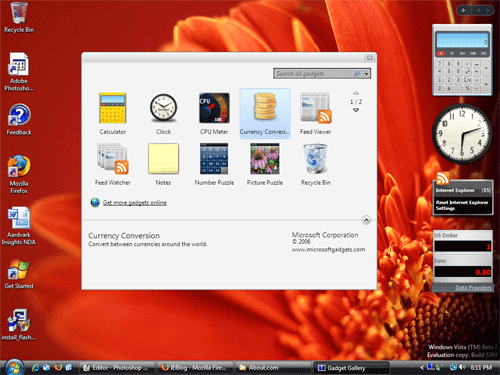
Windows Vista Sidebar
Windows 7 includes the same Windows Sidebar functions in Windows Desktop Gadgets although the sidebar no longer is present.
- Windows Desktop Reconfiguration
The Windows Vista/Windows 7 desktop can be visually and auditorily personalized by right clicking anywhere on the desktop and selecting Personalize from the pop-up menu. There are a large variety of of desktop items that can be changed to fit a user's personal tastes. Any change can be undone by selecting Default in the window where the setting was originally changed. The Personalization window provides options to change:
- Windows color and appearance - Windows, the Start menu, and the taskbar can all be assigned a different color and color intensity. Transparency can be enabled or disabled for these items.
- Desktop Background - The desktop background can be changed.
- Screen Saver - A picture or animation that covers the screen after a period of inactivity can be selected.
- Sounds - Different sounds can be chosen for operating system events such as when programs are closed, devices are connected, mail is received, printing is completed, etc. Standard Windows .wav files can be used, or personalized sound files can be used.
- Mouse Pointers - Non-default mouse pointers can be chosen for various activities.
- Theme - Themes are a background, set of sounds, icons, windows, etc. All of these items can be changed to a variety of different themes.
- Display Settings - Monitor resolution, refresh rate, color bit rate, and the video adapter used can be changed.
- Windows Search
Successor to XP's Windows Desktop Search (WDS), Windows Search includes more features.Windows Search is found in Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008. Also referred to as Instant Search enables users to more easily locate files, programs, browser favorites, saved instant messages, appointments, contacts, and e-mail messages by searching for file or folder names, properties, and even text contained within a file. Results are shown with the most frequently opened programs and files shown first. - Windows Control Panel
The Control Panel in Windows Vista/Windows 7 has a few upgrades from XP's version. The Control Panel menu has different titles and grouping for its various tools; however, the Control Panel can be switched to XP's Classic View. Tasks that have been recently done are grouped on the bottom left hand corner of the Control Panel in case they need to be used again. The same concept has been applied to all of the individual tool groupings. When a tool group is selected, the tasks for that particular group that have been used recently are also listed in the bottom left hand corner of the window. - Windows Vista Desktop Shortcuts
There are a number of keyboard shortcuts that can be used to configure the desktop, manage the desktop, and control the computer: - Users can lock the computer by pressing the Windows logo key
 and the L key.
and the L key. - Users can log off by pressing the
 key and the F4 key.
key and the F4 key. - Users can Restart the computer by pressing the
 key and the F6 key.
key and the F6 key. - Users can Shutdown the computer by pressing the
 key and the F8 key.
key and the F8 key. - Windows Sidebar can be started by pressing the
 key and the spacebar.
key and the spacebar. - Gadgets can be shown and cycled through by pressing the
 key and the G key.
key and the G key. - Windows Explorer can be started by pressing the
 key and the E key
key and the E key - The Run dialog box can be started by pressing the
 key and the R key.
key and the R key.
Previous run commands can be displayed and chosen when the Run dialog box is called by pressing the ![]() key and the R key along with the \ key.
key and the R key along with the \ key.
- Windows Instant Search can be started by pressing the
 key and the F key.
key and the F key. - The desktop can be displayed by pressing the
 key and the D key.
key and the D key. - Icons on the desktop can be resized by holding down the control key and moving the mouse scroll bar.
- Windows can be minimized by pressing the
 key and the M key.
key and the M key.
Quick Launch commands can be activated by pressing the ![]() key and the 1 key for the left most Quick Launch icon, the
key and the 1 key for the left most Quick Launch icon, the ![]() key and the 2 key for the second left most icon, etc.
key and the 2 key for the second left most icon, etc.
Taskbar and Start Menu
Vista's taskbar and Start menu control the programs and activities that a computer is working on. Understanding the functions of and being able to customize the taskbar and Start menu are essential skills for all computer users.
- Windows Taskbar
Windows's taskbar displays the Start Menu icon, Quick Launch icons, all programs that are open, the notification area, and the time.
The Quick Launch toolbar enables programs to be launched with a single click. Any program can be added by simply dragging the program's icon onto the Quick Launch toolbar or by right clicking the program's icon and selecting Add to Quick Launch.
The Quick Launch toolbar also has an icon called Show Desktop, which hides all open windows and displays the desktop, and a Switch between windows button which opens the Windows Flip 3D tool and allows a window to be selected and opened. The various windows can be cycled by pressing the and Tab keys. Windows can also be cycled through and selected using the more classic XP version by pressing the Alt and Tab keys.
and Tab keys. Windows can also be cycled through and selected using the more classic XP version by pressing the Alt and Tab keys.
Windows Vista Flip 3D
- Lock the taskbar so that it cannot be resized or unlock it.
- Auto-hide the taskbar so that it disappears unless the mouse pointer is over it or always have it on the desktop.
- Keep the taskbar on top of all other windows or have other windows cover it.
- Group similar taskbar buttons into one dropdown list or have all buttons displayed on the taskbar.
- Show or remove Quick Launch icons.
- Show window previews displays a thumbnail picture of running applications when the mouse pointer is over a button or just display a text title of the application.
The notification area displays icons that provide access to certain settings or the status of an operating system tool or a program. When the mouse pointer is over an icon, information about that particular icon will be displayed. Right clicking an option will diplay all possible options, and double clicking an option will open up that program or setting window.
Sometimes an icon in the notification area will display a pop-up window that will notify a user about an aspect of the system, such as wireless networks being available or new hardware being added. The notification area can be customized by right clicking anywhere on the taskbar selecting Properties from the pop-up menu, and selecting the Notification Area tab. The notification area can be customized by hiding inactive icons and by selecting to show or not show any of the notification icons.
The taskbar can be customized by right clicking on the Start menu, selecting Properties, and selecting the taskbar tab. There are six options available:

Windows7 Aero Peak and Snap
Vista's Taskbar thumbnails can be cycled through by pressing the ![]() key and the T key.
key and the T key.
- Windows Start Menu
The Windows Vista and Windows 7 Start menus are similar to XP's start menu, but they have a few differences beyond the 3D aspect of the buttons. There are options for locking the computer, putting it into low-power sleep mode, along with all shut down or log off options that are available without having to open the Turn Off Computer window and selecting them from a drop down list. Programs are also easier to open with a single click instead of the double click.
Windows Start menu can be customized by right clicking on the Start menu and selecting Properties. The first option that is available is to switch between the Classic Start menu which is similar XP's menu and customize it, or to stick with the Windows menu and customize it. Customization provides users to change options for how current icons are displayed, and provides options to remove the icons currently showing or to add icons such as: - Favorites
- Printers
- Run Command
- System Administrative Tools
- The number of recent programs that will be displayed
- The browser other than IE
- An email program other than Windows Mail
Customization also allows users to enable dragging and dropping of menu or submenu options to other locations on the Start menu, highlight newly installed programs on the Start menu, open submenus when the mouse pointer is paused on them, and make the Start menu icons larger.
Two other options available in the Start Menu Properties window are to store and diplay recently opened files or to not store and display them. This option is also available for recently opened programs.
Vista's Start menu, along with many of Vista's other visual features and tools, can be added to Windows XP by downloading these tools from a variety of sites on the Internet.
Main Features
Striving to offer a more secure environment for users and better graphical interface and media experience for Internet users, Windows Vista contains a vast number of changes and new features while Windows 7 seeks to upgrade these in more user friendly fashion.
With a large choice of media features, some may opt out of features that don't suit their needs. In order to turn features on or off, go to:
Start → Control Panel → Uninstall a program (Under the Programs heading) → Turn Windows features on or off.
Turning features off will not remove files from the hard drive, but any features or programs that run in the background use resources and should be disabled if it is not used. Some features can be security risks.If they are not needed, they should be disabled. A variety of features can be enabled or disabled:
- ActiveX
- Games
- Indexing Services
- Networking and Internet Services
- Security
- Printing
- Telnet
- Fax and Scan
- Windows Meeting Space
Many of the features are complex networking features that must be understood before turning them on or off, but others are simple features such as games, printing, faxing and scanning, and Windows Meeting Space. The more complex features require an understanding of networking protocols and technologies to discuss while the simpler features of Windows Vista is discussed in this lesson.
Communication
Windows Vista's communication tools have been improved in a number of different areas. Vista has improved Internet Explorer version 7.0, created a new email program that replaces Outlook Express, a new calendar tool, a new collaboration tool that replaces NetMeeting, and an updated messenger that replaces MSN Messenger.
- Windows Internet Explorer Version 7.0
Microsoft's Internet Explorer v. 7.0 (IE7) has a number of improved features over previous versions. Its name has changed from Microsoft Internet Explorer to Windows Internet Explorer. Internet Explorer version 7.0 has made some notable upgrades from version 6.0 in areas such as security and display.
Released in March 2009, Internet Explorer 8 (IE8) is the default browser for Windows 7. It also works on Windows XP and Windows Vista. Highest priorities for this browser are for greater simplicity of use and for better security.
- Security Features:
Fraudulent phishing scams aggressively attempt identity theft by masquerading as legitimate businesses in electronic communication. IE 7 fights Phishing by keeping a log of all known phishing sites and displaying a warning web page when these are visited. Web sites used to be authenticated by only having the server present an Extended Validation Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate, but IE7 now uses the more secure Transport Layer Security (TLS) for encrypting web sites and providing mutual authentication with the use of public key technology.TLS mutual authentication involves the use of a public key certificate. Add-ons such as ActiveX controls are disabled by default and can be activated on a case by case basis to ensure they are used only by trusted web sites. Another method of ensuring that trusted web sites remain trusted is IE's protection from hacked web sites. Even trusted sites can be hacked and malicious malware can be spread to visitors. IE 7 protects computers from these attacks.
- Display Features:
Tabbed browsing is the ability to display multiple web pages in one browser window. Each page creates a tab (much like a task bar) that can be selected to switch between web pages. All of the tabs can be displayed in miniature in one screen with the Quick Tabs feature. Groups of tabs can also be saved as one entry in the Favorites folder, making the organization of often used web sites much easier. Printing of web pages has also been improved. - Windows Mail
- Windows Calendar
- Windows Meeting Space
- Windows Live Messenger
 |
Windows Mail replaces Outlook Express, Windows previous default email program. It also helps with Phishing sites by detecting the fraudulent links that are often sent through email. Other new features include an improved junk mail filter, and an email search feature. |
 |
Windows Calendar keeps track of appointments and activities by sending reminders about tasks, events, and activities. Calendars can be shared so that schedules can be coordinated if necessary by giving access to other users or by publishing a Windows Calendar to a web-based calendar or network share. |
 |
Windows Meeting Space replaces Windows NetMeeting, which is a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and videoconferencing tool. Although Windows Meeting Space does not have the ability to set up audio or video conferences, it does add a collaboration feature. Users from any networked computer or an ad hoc wireless networked computer can join in a session and view or edit a presentation area that can contain a user's desktop, a program's display, or user comments. Audio and text conferencing features can be found in Windows Live Messenger tool, but NetMeeting must still be used for video conferencing unless a third party application is used. |
 |
Windows Live Messenger is an updated version of MSN Messenger that is used to send text and audio to other phones or computers. Files can also be shared to specified contacts. |
Media
Windows Vista has created or updated a number of media tools and features such as Windows Media Player 11, Windows Photo Gallery, and Windows DVD Maker. Vista also introduces a new technology called Windows XPS and an upgrade to video technology with DirectX version 10.
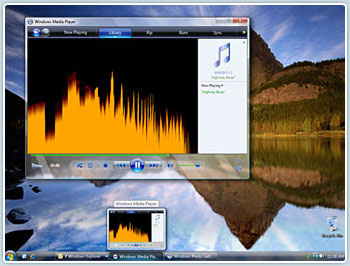
- Windows Media Player 11
- Windows Photo Gallery
- Windows Movie Maker
- Windows DVD Maker
 |
Windows latest Media Player version not only plays music and videos, but also rips, copies and facilitates the purchasing of music. Windows Media Player can also play videos or show images. |
 |
Windows Photo Gallery imports, organizes, edits, displays, and prints digital images. Organization has been improved by adding a tagging and indexing feature. Pictures can also be made into a video using Windows Movie Maker and Windows DVD Maker. |
 |
Windows Movie Maker adds effects, transitions, audio and text, along with titles and credits to create a slide show or movie out of imported images or video. Video can be captured from a camera or other device, and can also be imported. Video and audio formats that can be imported are .VOB, .AVI, .MPEG, .ASF, .WMV, .WAV, .WMA, .and MP3. |
 |
Windows DVD Maker creates video DVDs by transferring videos to DVD format. Menus, disc titles, lessons, notes, and publishing styles can all be added to DVDs. The quality and size of the video files, along with the option to output the video in widescreen or fullscreen are available with Windows DVD Maker. |
- Windows DirectX 10
- Windows XPS
Windows DirectX is a collection of APIs which provide services such as gaming controls, 3-D graphics rendering, web animation, video playback, and sound playback. DirectX is mostly used to develop computer games. The latest version has greatly improved the details and shading of images while decreasing the load placed on the CPU for processing graphics.
Windows XML Paper Specification (XPS) is a document storage and viewing specification that is similar to PDF. Windows XPS Document Writer enables documents to be saved in a standardized format or published in an easily viewable form. Similar to PDF documents, XPS also ensures that no one is able to edit an XPS document. XPS also performs printer control language (PDL) functions similar to PostScript.
Microsoft Management Console
First introduced in Windows Vista, the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) tool provides a shell that allows you to insert various tools to administer networks, computers, services, and other system components. This tool is also available in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2. Version 3.0 provides a number of improvements that make it easier to use:
- Action Pane – lists actions available, based on currently selected items
- New Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box – easier to manage adding, organizing, and removing snap-ins. This is the most noticeable improvement; snap-ins are the basic components in the management system.
- Improved error handling – provides warning for snap-ins that could make MMC fail and gives options to handle the situation
To access the MMC tool:
Click Start, click in the Start Search text box, type mmc, and then press ENTER.
 Managing Snap-ins in Windows Vista |
 Managing Snap-ins in Windows 7 |
Snap-Ins
Snap-ins are the basic components of Microsoft's Management Console (MMC). MMC snap-ins are the actual management tools. The console, sometimes referred to as a "tools host," is simply a framework into which snap-ins are added. MMC snap-ins are made by Microsoft and other companies.
Account Options
Windows user accounts allow multiple users to access one computer or any computer in a network situation. Security is an important aspect for any network or individual computer, so it is important to set up user accounts properly. The first account that is set up during installation is an administrator account. This account should be used to set up computer features and programs and to make administrative changes.
All other accounts that will be used for everyday computing should be set up as standard accounts. The third account option is for a guest account, which is created for users who will only require temporary access to a computer.
Windows requires at least one administrator account on a computer. If you have only one account on your computer, you can't change it to a standard account.
Adding and Removing Users
In order to add or remove user accounts for a workgroup or single computer, follow these steps:
- Step one:
Click on Start → Control Panel → Add or remove user accounts under User Accounts and Family Safety.
If the UAC prompts you for an administrator password, it must be entered in order to continue. - Step two:
Click on Create a new account to add an account, or select an account and click on Delete the account to remove an account. - Step three:
If an account is being created, enter the name of the user account, select a radio button of the account type that is to be assigned to the user, and click Create Account. - Step one:
Click on Start → Control Panel → User Accounts and Family Safety → User Accounts → Manage another account.
If the UAC prompts you for an administrator password, it must be entered in order to continue. - Step two:
Select the specific account that is to be changed and click on Change the account type. - Step three:
Select the radio button of the account type that is to be assigned to the specified user and click on Change Account Type.
Modifying Users
User accounts enable several users to share a single computer or to use any computer is a network setting. Each account will keep the user's unique program settings, operating system settings and preferences, and will also determine which programs can be accessed and changes that can be made to a computer. In order to modify the user account type for a workgroup or single computer, follow these steps:
Users / Security Groups
A user group is a collection of users who have all been assigned the same security permissions. Security permissions control access to system resources, programs installation and removal, and system tasks, User groups are also called security groups. The two most common groups are administrator and standard users, however there are other options:
- Administrator - Administrator users are able to use all available controls such as access to all folders and files; the ability to add, delete, or modify user accounts; install or remove programs, updates, services packs, and fixes; use Safe mode, etc.
- Standard Users - Standard users can access their own files and folders, run programs, install programs that don't require administrative rights, and change their password.
- Backup Operators - Backup operator users are able to access the backup program so that files and folders can be backed up or restored.
- Cryptographic Operators - Cryptographic operator users are able to perform cryptographic tasks.
- Guests - Guest users are only able to access their own files and folders.
- IIS_USRS - IIS_USRS users are able to work on the remote Internet Information Server.
- Network Configuration Operators - Network configuration operator users are abile to install and configure network features.
- Performance Log Users - Performance log users are able to use the Windows Performance Diagnostic Console to locally or remotely monitor performance counters, logs, and alerts.
- Performance Monitor Users - Performance monitor users are able to to use the Windows Performance Diagnostic Console to locally or remotely monitor performance counters only.
- Power Users - Power users are able to backup up, restore, replace, or take ownership of files, install or remove device drivers, and install or remove applications.
- Remote Desktop Users - Remote desktop users are able to logon using the Remote Desktop Connection.
- Replicator - Replicator users are able to replicate files across domains.
Add a User Account to a Group
A group of standard users who share the same security rights can be added to a user group, also called a security group. It is important to assign the proper access rights to users; user groups makes this process easier. Grouping users is also an essential time saver for larger networks with hundreds of users. This helps you to avoid granting the same access and permissions to multiple users at once.
To do so, install the Local Groups and Users Snap-in.
Only Vista Business or Ultimate - Windows 7 Professional and Ultimate can perform these steps. Assigning user groups beyond the basic standard or administrator accounts is not an option for Vista Home Basic or Premium nor is this available on Windows Home Basic or Home Premium.
- Step one:
Click on Start, type mmc into the search box to open the Microsoft Management Console (MMC), and press Enter.
If the UAC prompts you for an administrator password, it must be entered in order to continue. - Step two:
On the left pane of the MMC, click on Local Users and Groups. - Step three:
If the Local Users and Groups option isn't available, add it.
Click on File → Add/Remove Snap-in → Local Users and Groups → Add → Local computer → Finish.
Press OK to finish adding the Local Users and Groups option. - Step four:
Double-click the Groups folder. - Step five:
Right-click the desired group, and then click Add to Group. - Step six:
Click Add.
Type the name of the user account. - Step seven:
Click Check Names and then OK until finished.
 Assigning Accounts to Groups in Windows Vista |
 Assigning Accounts to Groups in Windows 7 |
One of Windows XP's security flaws was the fact that it made all users that were created administrator level accounts by default. This was exploited by hackers because a user with administrator rights has permissions to install programs. Some users with administrator rights unknowingly allowed and continue to allow malware to be installed.
UAC Elevation Prompt
Vista has changed the user setup process to protect computers and networks from malware that exploited the default administrator rights that were applied to each new user. Vista assigns administrator rights to the first user that is set up. Every user after this is given standard rights by default, which do not contain permissions to install programs or change settings that effect all users.
Standard users will need to be manually changed to either an administrator level account or assigned one of the security group settings discussed above. Even administrators will have to deal with User Account Controls when a program is trying to be installed on a computer, or when settings that effect all users are being changed such as Windows firewall or Windows Updates.
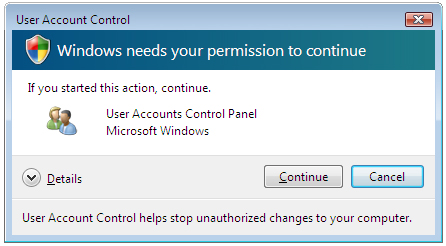
User Account Control Panel
The UAC checks a users security token, which is assigned to each user during logon. The security token contains the users privileges and security group membership, and determines what the user can and cannot do. Events that cannot be accomplished with a standard account can be carried out if an administrator level account password is entered. Even if an administrator level user attempts to change certain settings, the UAC will display an Elevation Prompt message that will inform the user that the action is being requested, provide details, and the user can either click on the Continue or Cancel buttons.
This occurs because an administrator's token is actually a split token. One half includes standard user permissions and is used during logon and while using the computer. When higher level permissions are required, the administrator half of the token is accessed by clicking Continue on the UAC Administrator Approval Mode Elevation Prompt window. This provides another layer of security.
Permissions that standard and administrative users have by default include:
Standard |
Administrator |
|---|---|
| Changing time zones | Installing and uninstalling programs |
| Changing power management settings | Installing a device driver |
| Creating and configuring Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections | Installing Windows updates |
| Establishing a Local Area Network connection | Installing an ActiveX control |
| Adding printers | Changing firewall settings |
| Establishing and configuring a wireless connection | Changing the date and time |
| Establishing and configuring a Bluetooth device | Changing Parental Control settings |
| Restoring backed-up files | Adding, removing, and changing a user's account type |
| Synchronization with a mobile device | Changing Automatic Updates settings |
| Modifying display settings and desktop background | Changing UAC setttings with the Security Policy Editor |
| Playing and burning of CD or DVD media | Changing Remote Desktop access settings |
| Configuring battery power options for laptops | Schedule Automated Tasks |
| Configuring Accessibility options | Restore backed-up system files |
| Changing own password | Working with system files |
| Set up and use the Remote Desktop feature | Working with audit logs |
The UAC Elevation Prompt can be disabled by following the steps in the simulations below.
Events that prompt the UAC to display the Elevation Prompt can be changed from their default settings by using the local Security Policy Editor tool (secpol.msc) found by using the path: Local Security Settings-->Local Policies-->Security Options. Administrators Access Mode can even be changed to have to input their password for the Elevation Prompt.
Events that prompt an Elevation Prompt are color coded to be application specific. If the application publisher is blocked by a policy or Windows, a red window bar appears. A splash background bar signifies a Vista published application, while a Microsoft verified publisher prompts a grey bar window. An unsigned program prompts an orange bar window.
